Fact: Our problem solving strategy has not changed. In fact, we can always use it to help us solve new problems!

Rough Guide for Solving Word Problems :
- Step 1. Read the problem carefully to determine what you are being asked to find.
- Step 2. Select a variable to represent each unknown quantity. Specify precisely what each variable represents and note any restrictions on each variable.
- Step 3. If necessary, make a sketch and translate the problem into a word equation or a system of word equations. Then translate each word equation into an algebraic equation.
- Step 4. Solve the equation or system of equations, and answer the question completely in the form of a sentence.
- Step 5. Check the reasonableness of your answer.
The Main Kinds of Problems: The following kinds of problems often lead to solving quadratic equations.
- Area Problems
- Problems involving Pythagorean Theorem
- Projectile Motion
- Number Problems
Area
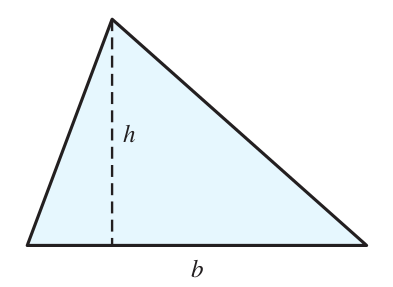
The base of a triangle (see the figure) is 1 m longer than the height. Find the base and the height if the area of this triangle is 65 m2. If necessary, round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Pythagorean Theorem: For any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the legs.
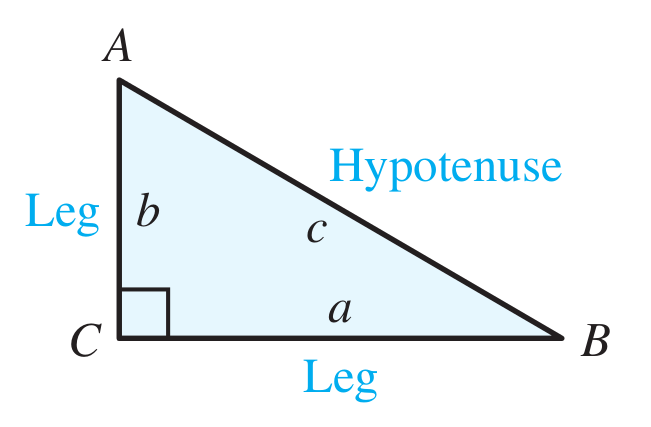
Pythagorean Theorem
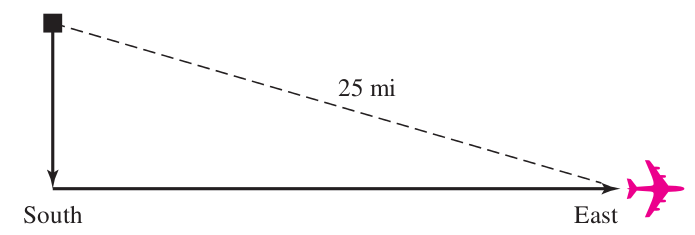
Example:Upon leaving an airport, an airplane flew due south and then due east. After it had flown 14 mi farther east than it had flown south, it was 25 mi from the airport. How far south had it flown? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Projectile Motion
Fact: When you throw an object in the air, it follows a parabolic path.
In fact, if the object's initial velocity is $v_0$, and its initial height $h_0$, the equation which describes its fight path is $$h(t)=-4.9t^2+v_0 t+ h_0$$ where the time $t$ is measured in seconds and the height $h$ is measured in meters.
Projectile Motion
Example: The height in meters of a ball released from a ramp is given by the function $h(t)=−4.9t^2+33t+28$, where t represents the time in seconds since the ball was released from the end of the ramp. How long will it take for the ball to hit the ground? If necessary, approximate to the nearest tenth of a second.
A Typical Number Problem
Example: Find two consecutive odd integers whose product is 99?