Examples of Linear Inequalities:
$5>-x+3$
$3(-3x-4) \leq -5(5x-1)$
$3x+2<-x+4$
Solutions to Linear Inequalities.
Example: Verify that $x=\frac{1}{2}$ and $x=-1$ are solutions to the linear inequality $3x+2 \leq -x+4$.
Example: Verify that $x=2$ is NOT a solution.
Question: What does the collection of all solutions look like?
Solving Linear Inequalities. Method 1: Algebraically.
Example: Solve the linear inequality $-2(-3x-1) \geq 4(-4x)$ algebraically.
Solving Linear Inequalities. Method 2: Graphically.
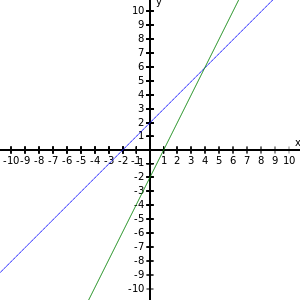
Example: Solve the linear inequality $x+2 \lt 2x-2$ graphically.
Solving Linear Inequalities. Method 3: Tables.
Example: Solve the linear inequality $3x+2\gt-x+4$ using a table.
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c} x & y_1=3x+2 & y_2=-x+4\\ \hline -1 & -1 & 5\\ \hline -0.5 & 0.5 & 4.5\\ \hline 0 & 2 & 4 \\ \hline 0.5 & 3.5 & 3.5\\ \hline 1 & 5 & 3 \\ \hline 1.5 & 6.5 & 2.5 \\ \hline \end{array} $$
Caution: When you divide by a negative, the inequality sign flips.
Example: $-4x+5 \gt 3x-5$
Costs and Revenue The daily cost of producing $x$ units of cellular phones includes a fixed cost of $\$$650 per day and a variable cost of $\$$12 per unit. The income produced by selling $x$ units is $\$$16 per unit. Letting $y_1$ represent the income and $y_2$ represent the cost, graph $y_1$ and $y_2$. Determine the values of $x$ for which $y_1>y_2$, the profit interval for this company.